Next: Package Data Abstraction Coupling Up: Coupling Previous: Locality of Data (
Message Passing Coupling ( )
)
Works with all instances of a common meta-model,
regardless of whether they were produced with the Java or the
UML front-end. The respective extends (Java) or
generalization (UML) relations expressing the inheritance
between two classes are mapped onto relations of type
inheritance in the common meta-model (and the - Handle

- Description
- The MPC measures the number of method calls defined in methods of a class to methods in other classes, and therefore the dependency of local methods to methods implemented by other classes. It allows for conclusions on the message passing (method calls) between objects of the involved classes. This allows for conclusions on re-useability, maintenance and testing effort.
- Scope
- Class
- View
-
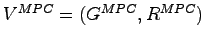
- Grammar
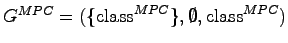
- Relations
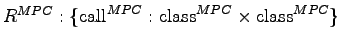
- Mapping
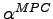 :
:
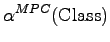
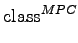


- Grammar
- Definition
-
The
 value of a class
value of a class
 is defined
as:
is defined
as:


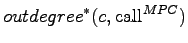
- Scale
- Absolute.
- Domain
- Integers
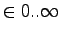 .
. - Highly Related Software Quality Properties
-
- Re-Usability 2.4
-
is negatively influenced by coupling.
- Understandability for Reuse 2.4.1:
-
A part of a system that has a high (outgoing)
efferent coupling may be highly inversely related
to understandability, since it uses other parts
of the system which need to be understood as
well.
Understandability decreases with increasing MPC.
- Attractiveness 2.4.4:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be highly inversely related to
attractiveness, since they are using other parts
of the system which need to be understood as
well, and represent dependencies.
Attractiveness decreases with increasing MPC.
- Maintainability 2.6
-
decreases with increasing MPC.
- Analyzability 2.6.1:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be highly inversely related to
analyzability, since they are using other parts
of the system which need to be analyzed as well.
Analyzability decreases with increasing MPC.
- Changeability 2.6.2:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to
changeability, since they are using other parts
of the system which might need to be changed as
well.
Changeability decreases with increasing MPC.
- Stability 2.6.3:
-
Parts showing a high (outgoing) efferent coupling
may be inversely related to stability, since they
are using other parts of the system, which are
can affect them.
Stability decreases with increasing MPC.
- Testability 2.6.4:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be highly inversely related to
testability, since they are using other parts of
the system which increase the number of possible
test paths.
Testability decreases with increasing MPC.
- Portability 2.7
-
decreases with increasing MPC.
- Adaptability 2.7.1:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to
adaptability, since they are using other parts of
the system which might need to be adapted as
well.
Adaptability decreases with increasing MPC.
- Related Software Quality Properties
-
- Functionality 2.1
-
is both negatively and positively influenced by
coupling.
- Interoperability 2.1.3:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be directly related to
interoperability, since they are
using/interacting with other parts of the system.
Interoperability might increase with increasing MPC.
- Security 2.1.4:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to security,
since they can be affected by security problems
in other parts of the system.
Security might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Reliability 2.2
-
might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Fault-tolerance 2.2.2:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to
fault-tolerance, since they can be affected by
faults in other parts of the system.
Fault-Tolerance might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Recoverability 2.2.3:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to
recoverability, since their data is distributed
in other parts of the system making their
recovery difficult.
Recoverability might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Re-Usability 2.4
-
might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Learnability for Reuse 2.4.2:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to
learnability, since they are using other parts of
the system which need to be understood as well.
Learnability might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Operability for Reuse - Programmability 2.4.3:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to
learnability, since they are using other parts of
the system, which represent dependencies.
Programmability might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Efficiency 2.5
-
might decrease with increasing MPC.
- Time Behavior 2.5.1:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to time
behavior, since they are using other parts of the
system, thus execution during test or operation
does not stay local, but might involve huge parts
of the system.
Time behavior might get worse with increasing MPC.
- Resource Utilization 2.5.2:
-
Parts that have a high (outgoing) efferent
coupling may be inversely related to resource
utilization, since they are using other parts of
the system, thus execution during test or
operation does not stay local, but might involve
huge parts of the system.
Resource utilization might get worse with increasing MPC.
- References
- Since
- 1.0
Next: Package Data Abstraction Coupling Up: Coupling Previous: Locality of Data (
