Next: Code Conventions Up: Documentation Previous: Documentation
Lack Of Documentation ( )
)
Works with all instances of a common meta-model,
regardless of whether they were produced with the Java or the
UML front-end.
- Handle
- Description
- How many comments are lacking in a class, considering one class comment and a comment per method as optimum. Structure and content of the comments are ignored.
- Scope
- Class
- View
-
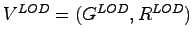
- Grammar

- Relations

- Mapping
 :
:

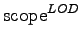
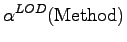



- Grammar
- Definition
-
The
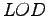 value of a element
value of a element
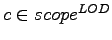 is defined
as:
is defined
as:
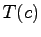


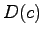





- Scale
- Rational.
- Domain
- Rational numbers
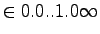 .
. - Highly Related Software Quality Properties
-
- Re-Usability 2.4
-
is inversely influenced by LOD.
- Understandability for Reuse 2.4.1:
-
Understanding if a class is suitable for reuse
depends on its degree of documentation.
Understandability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Learnability for Reuse 2.4.2:
-
Learning if a class is suitable for reuse depends
on the degree of documentation.
Learnability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Operability for Reuse - Programmability 2.4.3:
-
How well a class can be integrated depends on the
degree of documentation.
Programmability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Maintainability 2.6
-
decreases with increasing LOD.
- Analyzability 2.6.1:
-
The effort and time for diagnosis of deficiencies
or causes of failures in software entity, or for
identification of parts to be modified is
directly related to its degree of documentation.
Analyzability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Changeability 2.6.2:
-
Changing a class requires prior understanding,
which, in turn, is more complicated for
undocumented classes.
Changeability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Testability 2.6.4:
-
Writing test cases for classes and methods
requires understanding, which, in turn, is more
complicated for undocumented classes.
Testability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Portability 2.7
-
decreases with increasing LOD.
- Adaptability 2.7.1:
-
As for changeability 2.6.2,
the degree of documentation of software has a
direct impact. Each modification requires
understanding which is more complicated for
undocumented systems.
Adaptability decreases with increasing LOD.
- Replaceablity 2.7.4:
-
The substitute of a component must imitate its
interface. Undocumented interfaces are difficult
to check for substitutability and to actually
substitute.
Replaceablity decline with increasing LOD.
- Related Software Quality Properties
-
- Reliability 2.2
- decreases with increasing LOD.
- Re-Usability 2.4
-
is inversely influenced by LOD.
- Attractiveness 2.3.4:
-
Attractiveness of a class depends on its
adherence to coding conventions such as degree of
documentation.
Attractiveness decreases with increasing LOD.
- Maintainability 2.6
- decreases with increasing LOD.
- References
-
- LOD is implemented in the VizzAnalyzer Metric Suite.
Next: Code Conventions Up: Documentation Previous: Documentation
